One of the valid criticisms of online self-paced learning points out its passive nature. Online learners used to click through the course slides with little to no substantial feedback, and as passive recipients of information, they would feel less engaged. This, in turn, hurts their motivation, attention, and knowledge comprehension. On the other hand, traditional classrooms could offer so much more: discussions, group activities, hands-on projects, and timely instructor guidance, resulting in a more well-rounded educational experience.
Luckily, technology isn't standing still, and e-learning solutions are rapidly adopting new engaging, collaborative, and inquiry-based active learning methods. Interactive content has been instrumental in this transformation. Let's look into what types of interactive content exist, what benefits they offer, and how to incorporate them into one's training programs.
Benefits of interactive content
Interactive content refers to digital educational material that requires learners to engage with it to progress through the course - make choices and receive personalized responses based on their actions. As it paves its way into e-learning, it opens opportunities for more effective and impactful learning journeys for people across diverse domains and educational settings.
Here's what advantages interactive content brings to the table:
Enhanced engagement
One-way communication between the lecturer and the audience drains the learner's attention span and diminishes the retention level. Learners are more receptive to the subject matter when actively participating in the learning process, making them more motivated and interested. Breaking the monotony of traditional teaching methods with interactive content is one of the ways to engage learners, captivate their attention, and stimulate curiosity.
Enhanced retention
As learners get more invested in learning, they retain information better, leading to a more profound understanding of the concepts being taught. According to a study on e-learning effectiveness, active learning strategies such as fostering interactivity, lead to higher levels of engagement, resulting in improved academic performance and overall satisfaction with the learning experience.
Engaging with educational content through interactive exercises and simulations enhances learners' long-term memory retention compared to passive learning methods. And immediate feedback from interactive assessments allows learners to identify their strengths and weaknesses and correct their knowledge gaps on time.
Personalized learning paths
Interactive content enables adaptive learning experiences, catering to the diverse needs of individual learners. By analyzing learner-content interactions, instructional designers can track learners' progress, preferences, strengths, and weaknesses, customizing content delivery to suit each learner's learning pace and style.
A 2019 study of the students of the University of Burgos showed that personalized e-learning experiences improved learning outcomes and behavioral patterns and increased student satisfaction.
Enhanced evaluation and data-driven insights
Interactive educational tools have also been proven to assist the teaching and evaluation process. Interactive content generates valuable data-driven insights that enable instructional designers to measure learner progress, identify learning patterns, and refine course content. By analyzing learner interactions and performance metrics, designers can pinpoint areas where learners struggle the most, allowing them to make informed improvements to the learning materials. A case study published in the British Journal of Educational Technology revealed that data analytics from interactive learning platforms led to better-informed instructional design decisions and improved learning outcomes.
Active learning and critical thinking
Learners actively explore and manipulate information through interactive content, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Instead of passively absorbing information, learners are encouraged to analyze, synthesize, and apply their knowledge in practical scenarios. This active learning approach fosters deeper comprehension and long-term retention of information.
Fostering collaboration and social learning
Interactive content often incorporates collaborative elements, encouraging learners to interact with their peers, which fosters a sense of community and promotes social learning and knowledge sharing. Joint activities also prepare learners for real-world teamwork and improve communication skills, which are especially valuable in professional settings.
Real-world application
Interactive content bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills by providing learners with simulated real-world scenarios. A meta-analysis of educational technology's effectiveness found that computer gaming and interactive simulations resulted in higher cognitive gains than traditional methods across different domains and settings. By offering learners opportunities to apply their knowledge in practical contexts, interactive content prepares them for real-world challenges and enhances their problem-solving abilities.
The benefits of interactive content in education, such as increased engagement, enhanced retention, personalized learning, real-world application, and data-driven insights, are crucial aspects that contribute to the effectiveness of interactive content in enriching learning experiences. No wonder ed-tech companies are developing more and more tools for creating and managing interactive content.
Interactive content tools
As you can imagine, building interactive multimedia requires a particular set of tools with ranging levels of functionality, beginner-friendliness, and adherence to e-learning technical standards.
1. HTML5 and JavaScript libraries
HTML5 and JavaScript libraries, like Phaser and Three.js, are essential for building custom interactive content for web-based platforms. HTML5 provides a flexible structure for multimedia elements, while JavaScript is used to create interactive features. This combination allows instructional designers to develop interactive simulations, drag-and-drop exercises, interactive quizzes, and more. For developers and designers with programming skills, HTML5 and JavaScript libraries provide the flexibility to build custom interactive content for web-based platforms, allowing for tailored and innovative learning experiences.

Benefits:
- Flexibility to design interactive content tailored to specific learning objectives.
- Compatibility across various devices and browsers, ensuring a seamless learning experience.
- Extensive community support and a plethora of online resources to aid in development.
2. Multimedia editing software
Multimedia editing software, such as Adobe Premiere Pro and Camtasia, enables instructional designers to incorporate clickable hotspots, branching scenarios, and embedded quizzes directly into videos, engaging learners on a deeper level.
Benefits:
- Enhanced engagement through interactive video elements that keep learners actively involved.
- The ability to create professional-looking interactive multimedia content without extensive coding knowledge.
3. Authoring tools
Authoring tools are user-friendly platforms specifically designed for creating e-learning content. These tools often include templates and pre-built interactions, making it easier for instructional designers to create interactive content without starting from scratch.
Some of the most widely used authoring tools are:
- Articulate 360, which includes Storyline for creating interactive e-learning courses and Rise for responsive content development;
- Adobe Captivate with features for creating interactive simulations, branching scenarios, and responsive content;
- and H5P, an open-source platform with a vast array of interactive content types for LMSs and web-based platforms.
To figure out which of them better meets your needs, you may find this comparison of Adobe Captivate and Articulate 360 helpful.
Benefits:
- Intuitive interfaces that streamline the content creation process, reducing the learning curve.
- Wide-ranging interactivity options, from simple quizzes to complex branching scenarios.
- Compatibility with various file formats and LMS standards, ensuring seamless content integration and interoperability.
4. Learning management systems
Learning management systems are integrated platforms facilitating content delivery, management, and tracking learners' progress. Some LMSs come with embedded authoring tools, allowing instructional designers to create interactive content directly within the LMS environment. This integration streamlines the content creation and delivery process, offering a seamless experience for learners and instructors.
Opigno LMS is a prime example of a platform with an embedded authoring tool, namely, H5P integration. This integration provides seamless content creation and delivery, allowing designers to embed H5P content within their courses directly.
Benefits of Opigno LMS with H5P integration:
- Centralized content management with easy content organization and update.
- Seamless content delivery to learners.
- Ability to track learners' interactions and performance within Opigno LMS in real time.
- Built-in assessment tools to administer quizzes and interactive activities within the LMS.
- User-friendly content authoring with H5P's intuitive interface.
- Extensive library of interactive content types catering to diverse learning needs.
- Compatibility with SCORM and xAPI standards, enabling interoperability with other e-learning systems.
5. Augmented reality and virtual reality tools
AR and VR are cutting-edge technologies that offer immersive learning experiences by overlaying digital content in the real world (AR) or creating entirely virtual environments (VR). These tools transform how learners interact with content, providing realistic simulations and hands-on experiences, especially beneficial in technical and vocational training, where learners can practice skills in realistic environments.
Some tools, such as Unity3D or A-Frame, are used by professionals, while platforms like CoSpaces Edu enable learners to build and explore their own virtual worlds for educational purposes. And Google Expeditions library offers virtual field trips to various destinations, enriching learning experiences in geography and history.

Benefits:
- A realistic but safe environment for practicing skills and applying knowledge without real-world risks.
- The immersive, attention-grabbing nature of AR and VR content.
- Spatial understanding, especially in subjects like architecture, engineering, and geography.
- Memorable, multi-sensory learning experience enhancing memory retention.
The diverse array of tools for creating interactive content caters to various skill levels and requirements. By harnessing them, instructional designers can captivate learners, promote active participation, and facilitate meaningful knowledge retention, transforming education into a dynamic and immersive journey.
Types of interactive content
Now, let's see what you can create using the above mentioned tools. There is a wide array of interactive content formats and activities for every occasion that employ every media format under the sun: text, images, audio, video, 3D models, VR, etc. Below, we will explore ten prominent types of interactive content and provide examples, implementation scenarios, and recommended tools for each.
1. Polls, quizzes, exercises, assessments.
Quizzes, polls, and assessments evaluate learners' understanding of the subject matter, collect feedback, and measure learning outcomes. These fundamental interactive content components allow instructors to gauge learners' performance, promote active recall, and provide immediate feedback.
Examples:
- Opinion polls gather learner opinions on specific topics or course content to stimulate discussions.
- Multiple-choice questions prompt learners to select the correct answer from a list of options.
- Fill-in-the-blank tasks require learners to complete sentences or equations by filling in missing words or numbers.
- Drag-and-Drop exercises require learners to match items by dragging and dropping them into the correct categories.
- Crosswords is a gamified version of filling in tasks.
- Dialog cards and flashcards pair images with questions and answers for a quick and easy self-assessment.
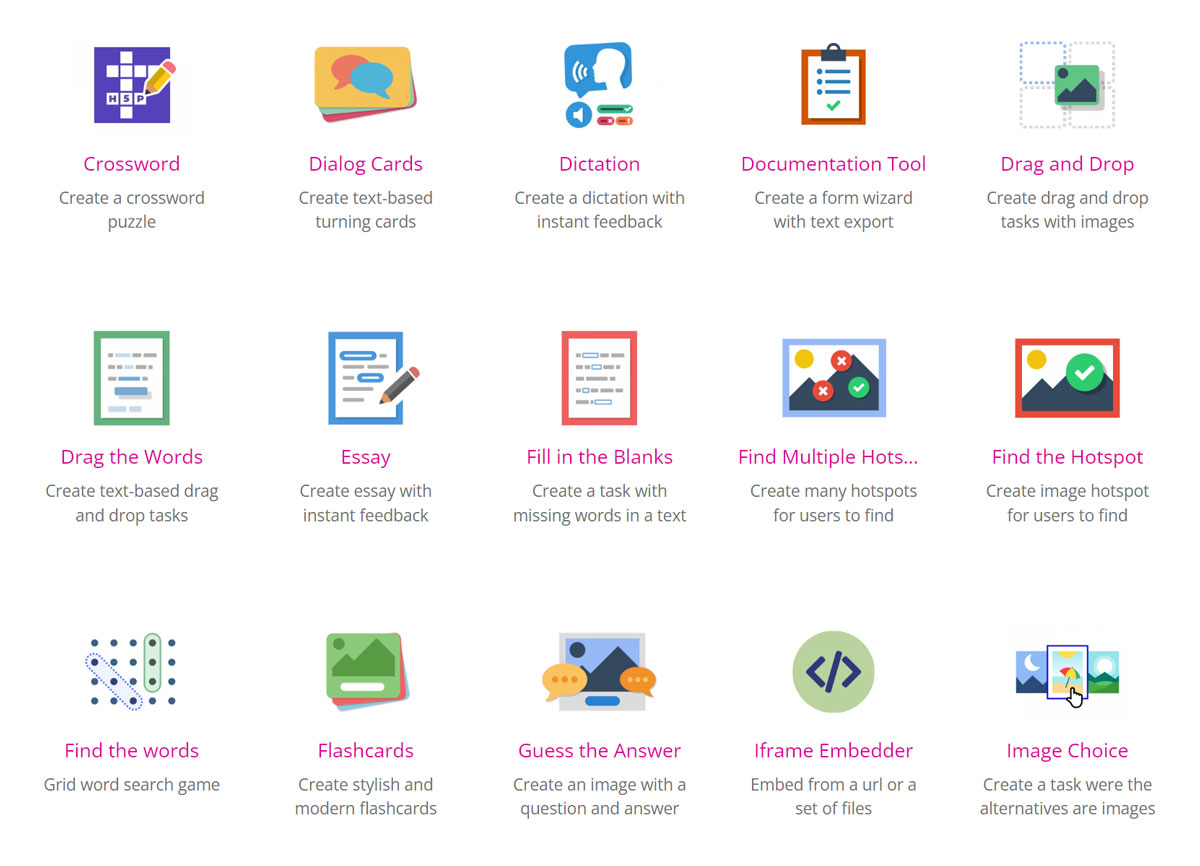
Application scenarios:
Quizzes and assessments are versatile and can be used across various educational settings, both formal and informal. Their primary purposes are formative and summative assessments with instant feedback, learners' feedback collection, and self-assessment.
In employee onboarding, quizzes can reinforce important information and identify knowledge gaps. Formative assessments measure learners' progress and identify areas for improvement. Knowledge check quizzes after each module assess and reinforce learners' understanding of a topic. And skill assessments and exercises evaluate learners' proficiency in a particular skill.
Implementation tools:
- Google Forms
- Kahoot!
- H5P Arithmetic Quiz
- Quizlet
- Articulate Quizmaker
2. Interactive infographics.
Interactive infographics allow learners to explore information visually, interact with data, and understand complex concepts more deeply.
Examples:
- Interactive charts and graphs help grasp data trends and statistics on a given subject.
- Clickable maps provide learners additional information on specific locations and other geographic data.
- Timelines unfold historical events and processes chronologically.
- Interactive anatomy helps learners to explore the human body by clicking on different body parts for detailed information.
 Application scenarios:
Application scenarios:
Interactive infographics are excellent for presenting statistical data, graphics, schemes, and interrelationships between different aspects of complex subjects engagingly.
Interactive visualizations can facilitate understanding geography and history, economy, physics, etc.
Tools:
- H5P Interactive Book
- Tableau
- Infogram
- Canva
- Adobe Illustrator
3. User-generated content.
Engaging learners in creating and sharing their learning materials drives deeper motivation, fosters a personalized and conscious learning experience, and improves material retention.
Examples:
- Interactive calculators can help learners solve mathematical problems, budgeting, or physics simulations and analyze how each input parameter affects the result.
- Interactive mind maps that learners create help them visualize relationships and connections between concepts.
- Blogging and reflective journals enable learners to express their thoughts on the course material and encourage critical thinking and self-assessment.
- Essays are used to qualitatively assess learners' understanding of the subject and reasoning skills.
- Virtual showcases of the learners' projects, research, or creative work to the class or community encourage public speaking and knowledge dissemination.
- Note-taking, e.g., Cornell-style notes, improves knowledge organization, retention, and consolidation.
With proper tools, learners can take and revisit notes within the e-learning platform. Source
Application scenarios:
User-generated content is ideal for promoting critical thinking and knowledge application. It's particularly effective for subjects where problem-solving and creativity are crucial, such as science and literature. User-generated interactive content can be applied across various e-learning settings, such as formal education, corporate training, or professional development programs. It is particularly effective in promoting learner autonomy, fostering creativity, and building a sense of ownership over the learning process.
Tools:
- Padlet
- Google Docs
- Lucidchart
- Calculator.net
- H5P Cornell Notes
4. Gamification elements.
Gamification is the integration of game-like elements into non-game contexts to motivate and engage learners. It taps into the intrinsic human desire for achievement and rewards, making the learning experience enjoyable and immersive. To learn more about gamification, check out our extensive overview here.
Examples of Gamification:
- Scoring and badges are earned by completing tasks, progressing through levels, or achieving milestones.
- Leaderboards display the top performers, which can foster healthy competition and encourage learners to strive for higher ranks.
- Unlockable content offers additional content or features as rewards for completing specific learning activities.
Application scenarios:
Gamification suits various subjects and industries, from corporate training to language learning. For example, in language learning, learners can earn points for completing challenges, and badges can signify language proficiency levels. Gamification is also effective for motivating learners in skill-building courses.
Tools:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) with built-in gamification features
- Gamification platforms like Bunchball, Gamify, or Gametize
- Axonify
- Classcraft
5. Interactive videos.
Interactive videos allow learners to interact with the content by making choices, answering questions, exploring different storylines, or just looking around, like in this 360 video:
Such interaction with enriched video content grabs learners' attention and enhances engagement and retention.
Examples:
- Embedded quizzes require learners to pause a video to answer questions or complete activities related to the content.
- Clickable hotspots contain additional information or resources on specific objects within the video.
- Decision points pause the video at certain moments and prompt viewers to make choices that determine the story's direction.
Application scenarios:
Interactive videos are effective for scenario-based learning, presenting complex topics in an engaging manner and providing personalized learning experiences. They are used for training, product demonstrations, and storytelling. E.g., interactive product demonstrations allow learners to explore product features and interact with virtual objects. Interactive training scenarios present real-life scenarios where learners can make decisions and see the consequences. For example, in sales training, interactive videos can simulate customer interactions, allowing sales representatives to practice their responses.
Tools:
- H5P Interactive Video
- Vizia
- Kaltura
- Articulate Storyline
- Rapt Media
6. Branching scenarios.
Branching scenarios present learners with decision points that lead to different paths and consequences, allowing them to explore different outcomes or personalize their learning journey.
Even a solution as simple as letting learners choose what chapter to study next can boost their involvement and sense of agency. Source
Examples:
- In language learning, offering different story paths and dialogue choices facilitates language practice.
- Compliance training can simulate real-world scenarios with multiple decision points.
- Customer service scenarios can train employees how to handle customer inquiries and complaints.
- Medical diagnosis scenarios emulate the process between the patient diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Application scenarios:
Branching scenarios effectively teach complex decision-making skills, critical thinking and enhance problem-solving abilities.
Tools:
- Twine
- BranchTrack
- Articulate Storyline
7. Collaborative activities.
Collaborative activities promote learner interaction, cooperation, and knowledge sharing through group projects, discussions, and peer feedback.
Examples:
- Group projects require learners to collaborate on shared assignments, projects, or case studies.
- Peer review encourages constructive criticism and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Discussion forums engage learners in discussions and sharing ideas.
Application scenarios:
Collaborative activities are valuable for fostering teamwork, communication, critical thinking, and social learning.
Tools:
- Google Workspace
- Slack
- Trello
- LMSs with social learning features
8. Augmented reality.
AR technologies offer immersive and interactive experiences, allowing learners to explore virtual environments by overlaying virtual elements in the real world.
Examples:
- In language learning, AR can be used to display translations of objects or learning materials in the learner's environment.
- Interactive simulations created with AR allow learners to visualize and interact with complex concepts or objects, e.g., the structure of molecules or the human anatomy.
- Workplace training can leverage AR for training employees on equipment operation, maintenance, or safety procedures by overlaying digital instructions or guides onto physical equipment.
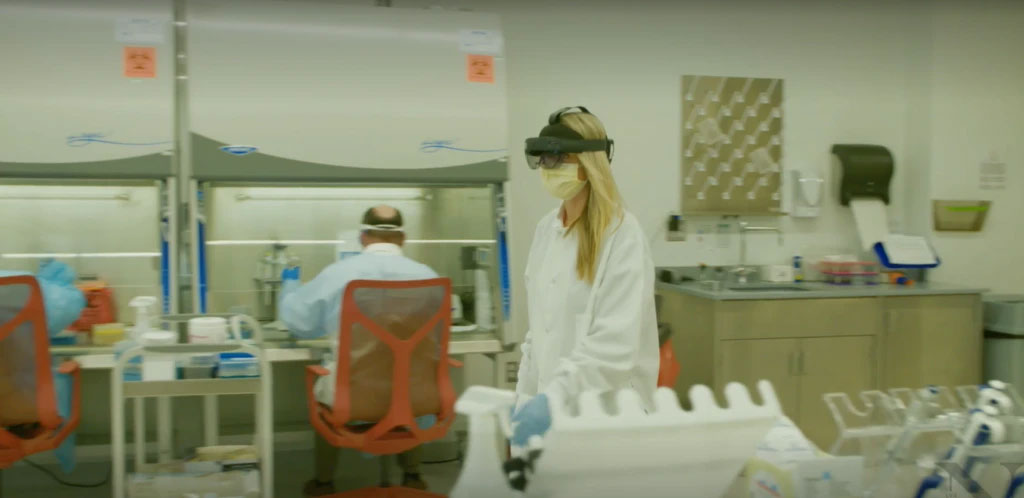

Application scenarios:
AR is highly effective for experiential learning, complex simulations, spatial understanding, skill acquisition, and providing realistic training environments. With its ability to bring abstract concepts to life and provide real-world applications of knowledge, AR bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds, making education more dynamic and impactful.
Tools:
- ZapWorks
- Unity XR
- H5P AR Scavenger
- Google ARCore
9. AI tools.
AI tools leverage artificial intelligence to recommend personalized content, offer real-time feedback, and provide intelligent tutoring.
Examples:
- Personalized learning paths suggested by AI take into account learners' performance and preferences.
- AI-powered chatbots provide instant answers, explanations, and guidance to learners.
- AI-driven assessments adapt difficulty based on learners' responses.
Application scenarios:
AI tools are particularly useful in providing personalized learning experiences, supporting self-paced learning, and offering immediate feedback.
For example, you can use voice recognition technology for exercises checking speaking skills. Source
There are many more ways and instances where AI can benefit e-learning. Check our comprehensive guide to learn how.
Tools:
- IBM Watson Assistant
- Area9 Lyceum
- Cognii
10. VR simulations and serious games.
Simulations and educational or serious games immerse learners in real-life scenarios, allowing them to practice skills and decision-making in a risk-free environment.
Examples:
- Flight simulators train pilots in various flight situations.
- Medical simulations allow medical students to practice surgeries and procedures.
- Cybersecurity games train employees to identify and prevent cyber threats through interactive gameplay.
- Sales scenarios roleplay enhances sales skills.
- VR field trips substitute excursions to museums, historical sites, or natural landmarks.
Imagine seeing Mona Lisa up close in the comfort of your home, with no crowds and long queues. Source
Application scenarios:
Simulations and VR are particularly valuable in technical training and hazardous professions, while the roleplay aspect of simulations is ideal for overall skill-based training and complex decision-making exercises.
Serious games are effective for skill development, employee training, compliance, behavior change, and increasing motivation in various domains.
Tools:
- Unreal Engine
- Unity3D
- H5P Virtual Tour
- Articulate Storyline
- Adobe Captivate
Leveraging various types of interactive content empowers us to create engaging and fruitful learning experiences. From quizzes to gamification to simulations, these interactive elements cater to diverse learning preferences and foster deeper comprehension, making the educational journey both enjoyable and productive.
Do's and don'ts for creating quality interactive content
No matter what interactive content format you want to implement in your courses, following certain steps can ensure you negate possible issues and get the best results.
Do's:
1. Defining learning objectives.
Clearly define the learning objectives before creating interactive content. Ensure each interactive element aligns with the desired learning outcomes, reinforcing key concepts and skills.
2. Accommodating diverse audience needs.
Conduct thorough audience analysis to understand learners' preferences, prior knowledge, and learning styles. Tailor the interactive content to cater to their specific needs and interests.
3. Designing for accessibility.
Ensure the interactive content is accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities. Follow accessibility standards and provide alternative multimedia (e.g., transcripts, captions).
4. Incorporating feedback loops.
Integrate immediate feedback mechanisms into interactive activities and formative assessments. Timely feedback reinforces learning and helps learners understand their progress.
5. Testing and iterating.
Before releasing interactive content, conduct testing with a diverse group of learners. Gather feedback and iterate based on user insights to enhance the effectiveness of the content continually.
Don'ts:
1. Overcomplicating design.
Strive for simplicity in interactive content design. Avoid overwhelming learners with complex interactions that distract from the core learning objectives.
2. Neglecting user experience.
Ensure a smooth and intuitive user experience. Clearly label interactive elements and provide straightforward navigation to prevent confusion.
3. Lack of adaptivity.
Leverage learner data and analytics to personalize the interactive content. Adapt the difficulty level, content sequence, or feedback based on individual progress and performance.
4. Underutilizing analytics.
Analyze data from interactive content to identify areas of improvement. Track learner progress, identify content gaps, and make data-driven decisions to enhance learner outcomes.
5. Overlooking professional support.
Collaborate with professional LMS developers and instructional designers with the technical know-how and creative flair to craft immersive, tailored learning experiences.
If you're ready to elevate your e-learning initiatives and take advantage of the benefits of interactive content, explore our e-learning platform demo and try out creating interactive content with an embedded H5P authoring tool.
Or, learn more about how we can help you revolutionize your e-learning journey with our instructional design services.
Published on August 15, 2023.